Technical terms of quality management: T
Taguchi
Genichi Taguchi (1924-2012) from Japan is one of the pioneers and important figures in quality science. His core activities were the “quality loss function“ and “experimental design“, also known as “design of experiments“.
Target costing
Cost planning system. The planned values are derived on the basis of prices that can be obtained on the market. It is important to know the customer expectations with regard to price and quality in order to break down the allowed costs (target costs).
Targeted sampling
Withdrawal of certain representative sub-quantities (samples) from a sampling unit. Here, a decision was made on the basis of information known in advance to take exactly these sub-quantities into consideration in the sampling. (On the basis of DIN 55350-14)
Task forces
Concept from the military sector. It is also used for project groups that are deployed to solve problems.
TAT
= Turn Around Time
In everyday language, TAT is defined as the time that a product takes to run through a process step or a chain of process steps. Example: A defective device‘s processing time in the repair department.
Taylorism
A methodology for breaking up workflows into smaller units to increase efficiency and effectiveness. Named after its founder, Fredrick Winslow Taylor (1856–1915).
TC
Technical Committee. Workgroup at the ISO for standards. See ISO/TC 176.
TCS
Total Customer Satisfaction.
Technical expert
Person who provides the audit team with special knowledge or expertise. This can be special knowledge or expertise regarding the organization, the process, the product, the service, the activity to be audited, the language or the culture. A technical expert is not an auditor in the audit team. (On the basis of ISO 19011:2018)
Technical rules
Recommendations, action guidelines or suggestions that demonstrate how laws, ordinances and technical facts can be implemented. Some examples of technical rules are DIN standards, VDE provisions, and VDI guidelines. They are essentially used to secure life, health and material goods, to protect the environment, and to ensure the quality of products and services.
Test
Characteristic values of one or more characteristics that are determined according to a procedure. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
TGA
Trägergemeinschaft für Akkreditierung GmbH, Frankfurt. The accreditation assignments were combined in a new structure in the DAkkS as Germany‘s national accreditation body as of January 1, 2010. The TGA entered the DAkkS via the DGA.
Theory of constraints
This theory, which was developed by the American physicist Goldratt, says that each system is limited in its performance by at least one element. The system‘s overall performance can only be improved over the long term by considering it as a whole.
Third party audit
Audit by external, independent organizations such as certification or accreditation companies, for example. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Throughput yield
In contrast to the term yield, throughput yield takes into account rework of nonconforming parts during production and does not include the reworked parts in the figure. Throughput yield accordingly determines the number of conforming parts without rework in the upstream process steps. Throughput yield is also called the first pass rate, which means the number of parts/products that pass through production in one pass (without rework).
Time to market
Time from the origination of a product idea until the finished product is introduced on the market. Reducing this time (product innovation, development, production, market launch, and marketing) is a crucial factor for competition.
TL 9000
Quality management model for the telecommunication industry. This standard adds to and adapts ISO 9001 to the requirements found in telecommunication. Its special feature is its inclusion of measurands into a management system. Performance figures must be reported on a regular basis. TL 9000 certification is strictly attended by ISO 9001 certification.
ToC
Tolerance
Upper limiting value minus the lower limiting value. (On the basis of DIN 55350-12)
Tolerance zone
Range of permitted characteristic values that are located between the lower and upper limiting values. (On the basis of DIN 55350-12)
Tools of quality
Top management
A person or group of people that directs and controls an organization at the highest level. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Total productive maintenance
System for maintaining production means. Behind this Japanese concept is the philosophy that the machine operator has a certain responsibility for the functionality of his/her workplace. This includes machines, tools and maintenance activities.
Total quality control
Quality strategy that comprises the entire company and that targets the customer needs. See Feigenbaum.
Total Quality Management
A concentrated focus of all company activities on (absolute) quality and dependability from the customer‘s point of view in line with the other corporate objectives. In particular, it strives for: an optimal competitive situation through improvement of the quality of products and services; improvement of the relation between costs and earnings; and greater employee commitment and qualification. This involves an analysis of the actual state, the detection of weaknesses until they have been completely eliminated, the continuous commitment to improvement in the entire company, and a systematic structuring of environmental relationships (natural and social environments). Success by means of TQM is based on the use of systematic methods and tools and the active participation of all employees. This total quality management definition makes it clear that it is more than just a corporate philosophy that has to be put into practice in order to motivate its implementation.
TPM
See Total productive maintenance.
TPS
Toyota Production System.
TQC
TQM
Traceability
Possibility to trace the history, application or location of the object that is being considered. Traceability of a product can refer to the origin of materials and parts, the processing sequence, or the distribution or location of the product after delivery. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
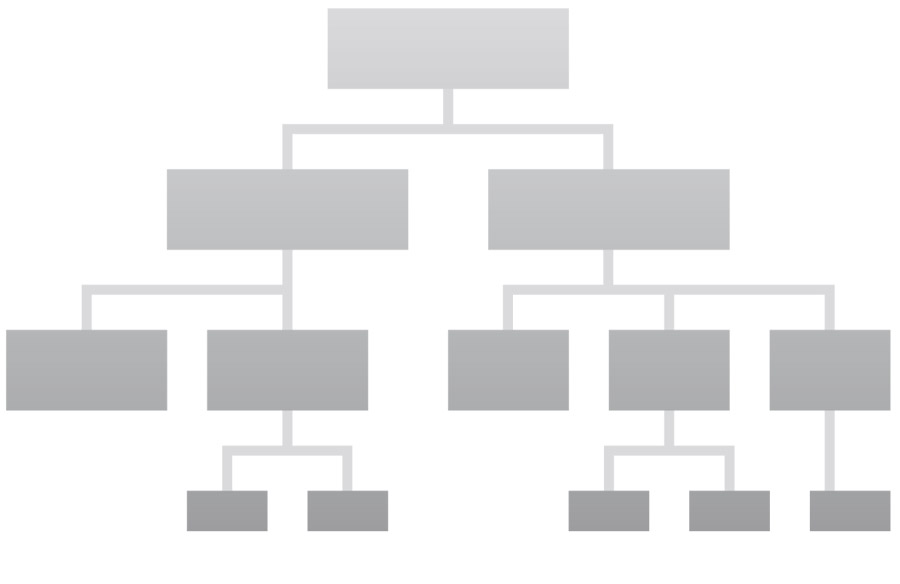
Tree diagram
Graphical representation that shows the correlations between individual elements in a network using connecting lines. As a result, relationships and hierarchical dependencies are made transparent. This representation‘s branched structure gives the tree diagram its name. The tree diagram is one of the Seven Management and Planning Tools (M7).
True value
Value of a quantitative characteristic or quantity. Most of the time, the true value is a theoretical concept and not known exactly. (On the basis of ISO 3534-2)
TS
Technical specification.
TTFF
Time To First Failure (see OTTFF). The operating time until the first failure.
Type test
Inspection of a product to test its suitability. (On the basis of DIN 55350-17)
