Technical terms of quality management: B
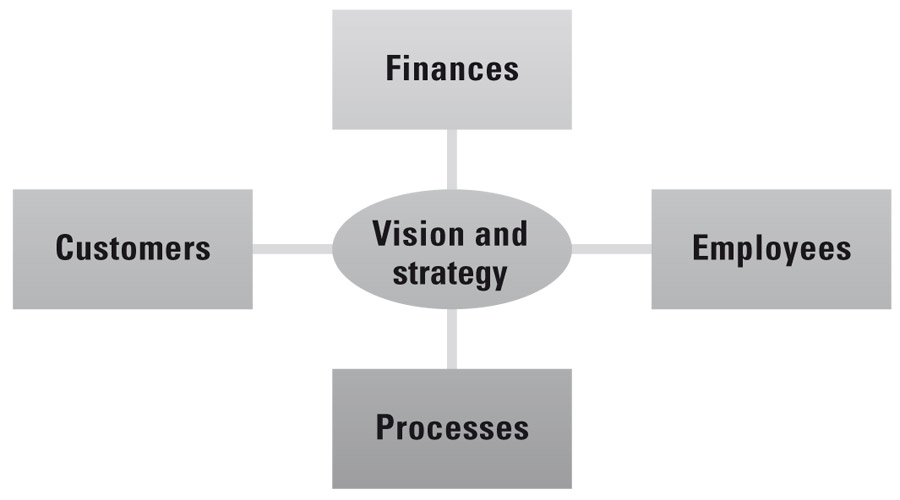
Balanced scorecard
A measuring instrument developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton to obtain a comprehensive overview of a company‘s performance and effectiveness. Beginning with the vision for corporate development (mission), the company‘s/organization‘s further strategic development is planned. The idea is to achieve a balance between the different perspectives for viewing a company‘s success: financial, process and customer perspectives, as well as the perspective related to learning and its effect on the company‘s potential. The scorecard itself is an indicator-based “simulation“ of networked company activities that allows individuals to evaluate their behavior and act in accordance with the strategy.
BAM
Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung, Berlin. [German Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing]
Bar chart
Graphical representation of data in the form of bars.
BAuA
Bundesanstalt für Arbeitsschutz und Arbeitsmedizin [German Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health], Dortmund.
BCS
British Calibration Service. Also see UKAS.
Benchmarking
The comparative check of products, services or processes using self-determined (internal) or specified (external) indicators (benchmarks). As a management method, benchmarking refers to a quality inspection with regard to leading competitors in order to improve a company‘s own competitive position. This can pertain to technical aspects of the product, to customer service or also to the company‘s presentation in its environment. The objective is to determine a “best practice“. In a wider sense, benchmarking refers to any kind of learning from comparison partners, for instance, also from companies in fields other than the company‘s.
Best settings
The term is used to classify the optimal setting of the most important input variables (see also: Red X). Within the Six Sigma DMAIC cycle, this is used in the improve phase.
Beta test
A product‘s last test phase before delivery to the customer or dealer. The software industry uses the beta test phase to test the stability and freedom from defects in the most economical way possible and also releases software to customers ahead of time (at no charge).
BetrVG
Betriebsverfassungsgesetz [German Works Constitution Act]
BGB
Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch [German Civil Code].
BGBl
Bundesgesetzblatt [German Federal Law Gazette].
Black Belt
Six Sigma expert who concentrates on project execution in a company. These experts are permanent members in Six Sigma projects and provide the team with knowledge and experience on the correct selection and use of the various tools and methods. As a rule, large or strategically important projects are headed by a Six Sigma Black Belt.
BNetzA
Bundesnetzagentur für Elektrizität, Gas, Telekommunikation, Post und Eisenbahnen, Bonn. [German Federal Network Agency for Electricity, Gas, Telecommunications, Post and Railway]. The organization was established on January 1, 1998 as regulators for telecommunication and post (RegTP) and renamed the Bundesnetzagentur [German Federal Network Agency] on July 13, 2005. It is the regulatory body responsible for maintaining and promoting competition in network markets. www.bundesnetzagentur.de
Bonus-malus system
System that rewards good performances (bonus) and penalizes poor performances (malus). This system can also be associated with financial quantities.
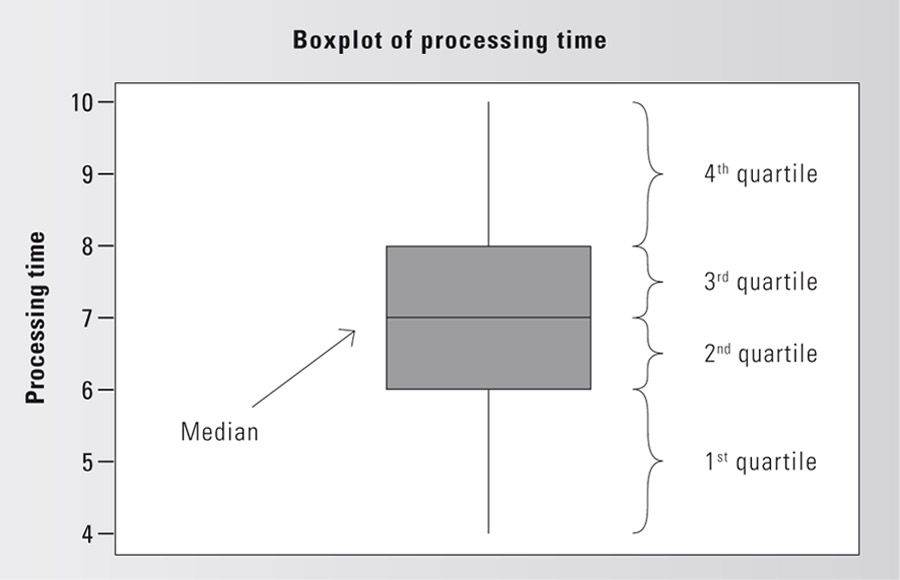
Box plot
Graphical evaluation of the dispersion and distribution of data. It must be noted that the data are divided into four quartiles, i.e., 25% of the data is combined into one quartile.
The gray box (see graphic) corresponds to the area in which the middle 50% of the data lies. The box plot representation shows the median and not the arithmetic mean.
The antennas above and below the box represent the data values that lie outside the box in the 1st and 4th quartile.
BPM
See Business Process Management.
BPO
Business Process Optimization.
BPR
See Business Process Reengineering.
Brainstorming
(Q 7) quality tool: Method for finding ideas. In this process, a team tries to collect as many ideas, thoughts and suggestions for solutions as possible for a given problem. Initially, the ideas are only noted, but not evaluated. During this creativity phase, the idea is to collect as many ideas as possible. These are discussed, sorted and evaluated in the second step (evaluation phase).
Breakthrough strategy
BS
British Standard.
BSC
BSI
- Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik [German Federal Office for Information Security], Bonn. www.bsi.bund.de
- British Standards Institution, London. www.bsigroup.com
Business Excellence
See Excellence models, Total Quality Management.
Business process
Process that is determined by the customers‘ specific requirements and that produces a benefit (value creation) for both the customer and the organization providing the product or service. A business process is consequently a procedure for solving customer problems.
Business Process Management
Planning, organization and monitoring of a company‘s processes in terms of quality, time, costs and customer satisfaction. The objective of this management concept is to optimize and automate business processes to a large extent.
Business Process Reengineering
Concept to refocus companies: Fundamental change in the company sequences with the objective of completely restructuring all relevant processes. The processes should be redesigned in order to achieve the greatest possible efficiency.
