Technical terms of quality management: E
EA
European Co-operation for Accreditation, Paris. Independent, nonprofit organization that in particular represents the interests of the European accreditation bodies.
www.european-accreditation.org
ED
Experimental Design. See Design of Experiments.
EEA
Effectiveness
Degree of success that indicates extent to which planned activities are realized and planned results achieved. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Efficiency
Degree of efficiency. This describes the relation between an achieved result and the resource deployed for it. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2001)
EFQM
Former European Foundation for Quality Management with headquarters in Brussels. The EFQM was established in 1988 and today is a non-profit organization for business excellence with more than 600 member companies in around 40 countries. The objective is to provide the member companies with information about business excellence and to strengthen the networking of the companies. In 1991 the EFQM established the prestigious EFQM Excellence Award. The EFQM presents this quality award annually to companies that achieve outstanding results. The EFQM is furthermore the guardian of the EFQM model, which serves as a guideline to help companies succeed on the markets and also to measure this success. www.efqm.org
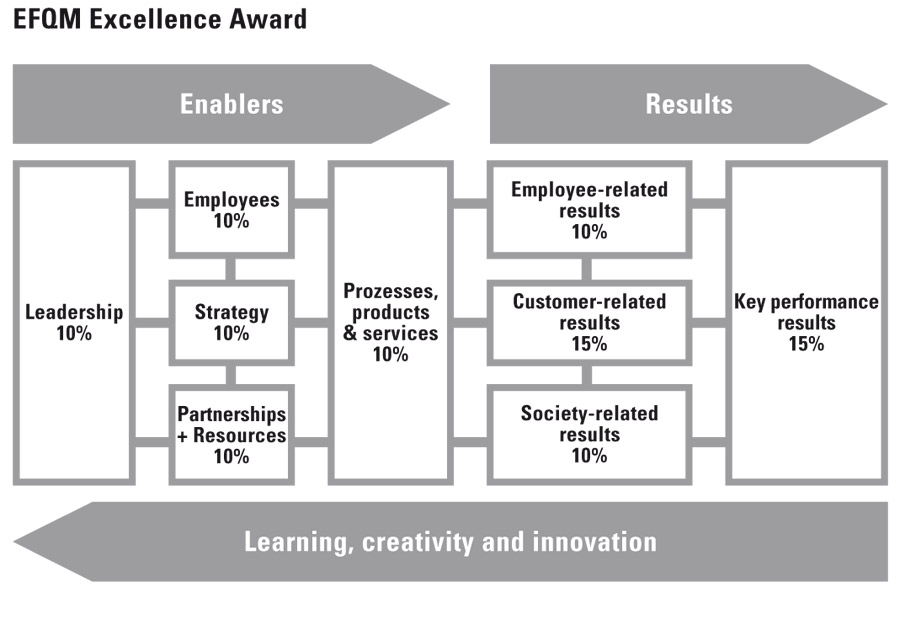
EFQM Excellence Award
European quality prize that the EFQM has awarded to companies annually since 1991 as the highest recognition for outstanding achievements and excellence. The companies are rated on a system with a possible 1000 points which is divided into the nine categories: Leadership; Strategy; Employees; Partnerships/resources; Processes, Products & Services; Customer-related results; Employee-related results; Society-related results; and Key performance results.
EichG
Eichgesetz [German Weights and Measures Act). Law covering measurement and verification.
EMAS
Eco Management and Audit Scheme. Requirements to be met by companies that voluntarily participate in a European Community system for environmental management and the internal environmental audit. A procedure that applies throughout Europe with the objective of continual improvement of the company‘s environmental protection. Regulation (EC) No. 1221/2009 forms the basis.
Employee focus
Basic attitude in an organization that is focused on considering each individual employee as a significant potential for solving problems and contributing creativity and on treating each employee accordingly. Management is responsible for creating an environment in which people can develop their abilities and consequently contribute to value creation in the company. Employees should be included in structuring the processes in order that they can release their potential and contribute their abilities. The objective is to use the employees‘ know-how for continual improvement (CIP) of all processes with regard to quality and productivity. (See Quality management principles).
Employee suggestion plan
Instrument for encouraging the capacity and willingness for innovation in a company‘s employees. In many instances cash and other awards are given as an incentive for employees to submit improvement suggestions. This instrument is primarily used in order to achieve innovations in products and processes in small steps, to encourage employee motivation and development, and to make a positive contribution to a goal-oriented corporate culture and culture of innovation. Employee suggestion plans have a long tradition in Germany. The idea was mentioned for the first time in a general regulation at the company Krupp in Essen in 1872.
Empowerment
Transfer of competencies and assignments previously reserved for managers to employees. This can improve employee and customer satisfaction.
EMS
See Environmental management system.
EN
European norm. (Standard from the CEN – Comité Européen de Normalisation)
Endangering analysis
A procedure stipulated in the framework of European directives and the national legislation on occupational health and safety based on these directives that forms the foundation of endangering judgment. Endangering analyses determine possible hazards and are to be conducted in according with the Arbeitsschutzgesetz [Occupational Health and Safety Act] or where appropriate in accordance with the Biostoffverordnung [Biomaterial Regulation] and the Gefahrstoffverordnung [Hazardous Substances Ordinance].
Endangering judgment
An evaluation required pursuant to Section 5 Arbeitsschutzgesetz [German Occupational Health and Safety Act] of the hazards for the employees associated with their work and the determination of required occupational health and safety measures. Each workplace is to be assessed in accordance with the legal specifications. There has also been an obligation to provide documentation since 1997. The judgment is often made according to typified workplaces (chemical or physical laboratory, mechanical workshop, etc.) and includes the assignment to endangering classes.
Engagement of people
You can find out more about this in the Quality management principles.
Environment
The environment, both natural and as changed by people, in which an organization or company is active (air, water, soil, flora, fauna, and natural resources).
Environmental management
All planning and actions that concern the dealings with the natural environment characterized by environmental protection affairs and perspectives. Environmental protection is law at the national level and is standardized in the framework of European directives and international agreements. Environmental management today therefore primarily includes the fulfillment of numerous requirements and conditions. Newer management theory also defines environmental management as the analysis, control, and planning of all external relations of the company as a system.
Environmental management system
The part of the management system that is responsible for implementing the company environmental policy, which today largely has to comply with national, European or international laws, directives and guidelines. The basis is formed by instructing standards such as the environmental management standard ISO 14001. These contain requirements such as for a written specification of a company environmental policy (which must include compliance with requirements resulting from environmental law) and for the designation of people responsible for tasks related to the environment. Many organizations have their environmental management system certified by external experts in order to increase their ecological credibility with the public and with their customers.
EOQ
European Organization for Quality, Brussels. European (non-profit) organization with the objective of effective improvement in the quality management area. The EOQ sees itself as a coordinating body for its member organizations. It was founded in 1956 and currently has 30 national European quality organizations, institutions, companies and individual people from all around the world. www.eoq.org
EPA model
Enterprise Process Architecture: Reference model for processoriented, service-based company architectures. This model is used to analyze different approaches to integration and to transfer them into a uniform model.
EQA
ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning. ERP characterizes a company‘s task to use resources in the company efficiently for business operations. ERP systems consist of complex application software to support resource planning.
Error margin
Limiting amounts of deviations for errors of measurement in the measuring instrument. (On the basis of DIN 1319-1)
Error of measurement
Deviation of the (uncorrected) measurement result from the reference value, where this can be the true value, the correct value or the expected value, depending on the definition or agreement.
(DGQ Volume 11-04:2009)
Estimator
Characteristic used to estimate a probability distribution parameter. (On the basis of DGQ Volume 11-04:2012)
ETA
Event Tree Analysis.
ETSI
European Telecommunications Standards Institute, France.
European Quality Award
The European Quality Award was renamed the EFQM Excellence Award (EEA) in 2006. See EEA.
Evaluation
- Selection, analysis and consolidation of data.
Remark 1: The selection of data is frequently used to describe trends.
Remark 2: Evaluation frequently allows actions to be prioritized. (DGQ Volume 11-04:2009) - Description, analysis and assessment of processes and organizational units. Focus areas can be the context, structure, process and product (result). The term originally comes from the Latin word “valuare“, which roughly means “to assess.“
Evaluation matrix
Evidence
Objective evidence: Data which confirm the existence or truth of something. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Evidence-based decision making
You can find out more about this in the Quality management principles.
EVOP
Evolutionary Operation of Processes. Analysis of process data with small dispersions within the parameters (variant of DoE).
Excellence models
The approaches to quality management systems on the basis of the ISO 9000 family of standards and the excellence models for organizations are based on common principles. Both approaches allow an organization to identify its strengths and weaknesses. They furthermore contain possibilities for evaluation using general models, offer a basis for continual improvement, and allow external recognition.
The fundamental difference between the two approaches to quality management systems in the ISO 9000 family of standards is found in their scope. The ISO standards formulate requirements for quality management systems and instructions for improving performance. The fulfillment of the requirements is determined by evaluating the quality management system.
The excellence models contain criteria that can be used to perform a comparative evaluation of the performance of organizations. They are suitable for all of an organization‘s activities and interested parties. The evaluation criteria in the excellence models consequently provide an organization with a basis for comparing its performance with that of others. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Expectation
For discrete variates, the sum of the products of all numerical values xi of the variate X and of the associated probabilities pi; for continuous variates the corresponding integral.
(DGQ Volume 11-04:2009)
External provider
A provider which is not part of the organization. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
External quality audit
See Second-party audit, Third party audit.
Externally provided processes
Selected processes or parts of processes which the organization does not execute itself but are externally provided. These processes are characterized by being required by the quality management system. The organization remains responsible for the output of these processes. It is up to the organization to control externally provided processes to make sure that they fulfill such requirements. (See also ISO 9001:2015)
Extreme value
Smallest or also largest individual actual value. (On the basis of DIN 55350-12)
