Technical terms of quality management: I
IAF
International Accreditation Forum, Cherrybrook (Australia). Global organization of accreditation companies that are active in the area of the accreditation of management systems, products, services, personnel or other programs. www.iaf.nu
IAOB
International Automotive Oversight Bureau in the USA. The members comprise Chrysler, Ford Motor Company, General Motors and the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG). One area that the work focuses on is management of the IATF 16949:2016 automotive standard. www.iaob.org
IAQ
International Academy for Quality, Milwaukee (USA). Global, independent, non-profit organization of quality issues specialists. www.iaq.org
IATF
International Automotive Task Force. Workgroup of the large automakers and their suppliers for the harmonization of nationally introduced quality management methods and of the quality management standards.
Their objective is to improve the product quality for automobile customers around the world. In Germany the VDA is the IATF member.
www.iatfglobaloversight.org
ICC
International Chamber of Commerce.
www.iccwbo.org
IDDOV
Identify – Define – Design – Optimize – Validate
Project management method within Six Sigma which plays a role in the development of new processes.
IDEA
Identify – Design – Evaluate – Affirm
Project management method within Six Sigma which plays a role in the development of new processes.
IDOV
Identify – Design – Optimize – Validate
Project management method within Six Sigma which plays a role in the development of new processes.
IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission. International standardization committee with headquarters in Geneva for standards in the field of electrical engineering and electronics.
IECQ
IEC Quality Assessment System for Electronic Components.
ILEP
Initiative Ludwig-Erhard-Preis – Auszeichnung für Spitzenleistungen im Wettbewerb e.V., Oberursel bei Frankfurt. Organization that awards the Ludwig Erhard Prize each year. www.ilep.de
Improvement
Activity for the enhancement of performance. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015). You can find out more about this in the Quality management principles.
IMS
See Integrated management system.
In-process inspection
Quality inspection that is performed during the manufacture or processing of a unit. (On the basis of DIN 55350-17)
Incoming inspection
Inspection of incoming goods at the request and with the participation of the customer or its representative. (On the basis of DIN 55350-17)
Indirect communication behavior
Also “Active listening“. Instead of steering the talk according to his/her own ideas, the auditor guides it according to what he/she can gather from the statements of the employee or auditee. The auditor attempts to see the content through the employee‘s eyes in order to be able to understand the employee‘s actions. This is the form of discussion that allows the employee to contribute the most.
Information
Significant data.
Information management
Management in the company with regard to information and communication: it comprises all management tasks related to information and communication.
Infrastructure
Basic equipment of a human resources, material or institutional manner (e.g., also services) that are necessary in order for an organization to function. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Inherent characteristic
Inherent means “existing as an essential constituent or characteristic of a unit.“ An inherent characteristic is one that is permanently associated with a unit.
If an inherent characteristic changes, the unit‘s function also changes. Example: Material and thread pitch of a screw are inherent characteristics. (See Condition)
Innovative process chain optimization
System for optimizing process chains: quality techniques and creativity techniques are networked.
Inspection
Conformity evaluation using observation and assessment. This activity can also be accompanied by measurement, testing or gauging. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Inspection by attributes
A decision as to whether or not the inspection lot can be accepted is made on the basis of the determined number of nonconforming units or the number of nonconformities in a sample. (On the basis of ISO 3534-2)
Inspection by variables
Acceptance sampling inspection: Inspecting an item by measuring the magnitude of one or more of its characteristics. (On the basis of ISO 3534-2)
Inspection characteristic
Property that is inspected. (On the basis of DIN 55350-12)
Inspection costs
Costs due to inspections conducted as scheduled (and not caused by nonconformities). Inspection costs include the costs in all of the organization‘s areas for the deployed personnel for inspections, the associated inspection, measuring and test equipment and the control of inspection, measuring and test equipment. Proportional costs for inspection activities are then to be assessed when inspection and other activities overlap in time. (On the basis of DIN 555350-11)
Inspection instruction
Inspection plan with stipulations regarding the inspection activities and inspection processes.
(DGQ Volume 11-04:2009)
Inspection list
The inspection list (check sheet) is a quality tool (Q 7) for recording data (nonconformities) efficiently and for presenting them clearly according to the type and number. The data are assigned to a nonconformity category and quantitatively recorded in a table. Problems in paint system
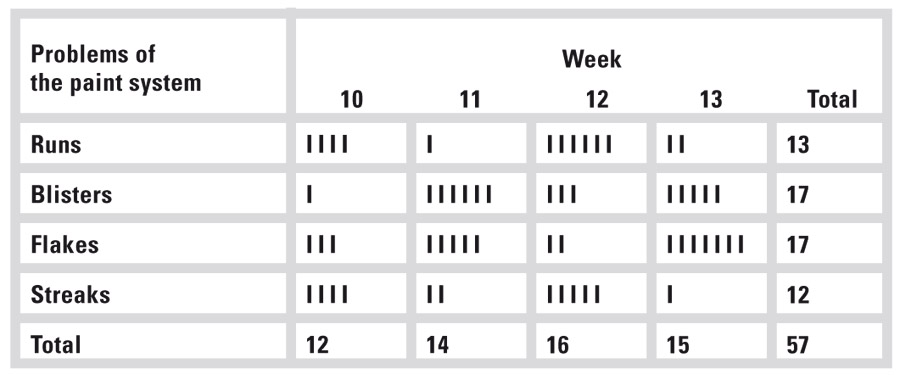
Inspection lot
Limited quantity or number of a product that undergoes a quality inspection that forms the basis for the evaluation of the totality.
Inspection plan
Specification for a single inspection or for a series of inspections. Inspection plans can contain different elements, such as inspection specification, inspection instruction and inspection schedule or they can refer to the same. This depends on the use of language in the particular organization. (On the basis of DIN 55350-11)
Inspection schedule
Inspection plan stipulating of the sequence of inspections.
Inspection specification
Inspection plan with stipulations regarding inspection engineering.
Remark 1: An inspection specification can also additionally contain stipulations regarding inspection activities and inspection processes as well as regarding the sequence of inspections.
(DGQ Volume 11-04:2009)
Inspection status
Status of a unit. It indicates which inspection or inspections were conducted on this unit, and with which results. (On the basis of DIN 55350-11)
Inspection, measuring and test equipment
Measuring systems for quality inspections
(DGQ Volume 11-04:2009)
Integrated management system
Consolidation of fragmentary or discipline-specific management systems (such as quality, environmental or occupational health and safety management systems) into an integrated management system. (On the basis of ISO 19011:2018)
Interacting processes
Processes that influence one another. ISO 9000:2015 calls the process approach the use of a system of processes in combination with identifying, understanding and managing interrelated processes.
Interaction plot
An interaction plot is a graphical tool that is used when there is a change in more than one factor in a statistical experiment design in order to analyze if these factors influence one another and if there are interrelations. Like the Main effect plot, the Interaction plot is used in the Improve phase in the Six Sigma DMAIC cycle.
Interest groups
Interested party
Group or person who has an interest in an organization‘s performance or success. A group can comprise an organization, a part of an organization, or several organizations. As examples for an interested party, the standard lists: customers, owners, people in an organization, suppliers, bankers, unions, partners or society. (On the basis of ISO 9000:2015)
Internal customer-supplier relationship
An internal customer-supplier relationship exists when departments or areas that receive a performance from other areas within an organization are seen as internal customers. This makes employees both customers and internal service providers or suppliers.
Internal quality audit
Internal reports
Compilation of product-related records that are necessary or helpful for planning, management and inspections.
Note: Internal reports on quality, environmental protection and occupational health and safety are prepared on a regular basis and as required. Examples are test reports, test certificates, inspection charts, quality control charts, investigations of the trend of the characteristic values of critical characteristics depending on the time.
(DGQ Volume 11-04:2009)
International Telecommunication Union
Internationale Fernmeldeunion (International Telecommunication Union or Union internationale des télécommunications, UIT) with headquarters in Geneva. Agency of the United Nations that deals with the technical aspects of telecommunication. This group defines international and globally effective standards. www.itu.int
Interrelationship digraph
The interrelationship digraph is a management tool (M7) that is used to illustrate interrelationships. The relationships among the causes of a central problem are shown by means of arrows. The causes are also classified according to their significance. The result is a representation of a problem‘s main causes as well as the relationships between them. It is then easy to derive possible solutions.
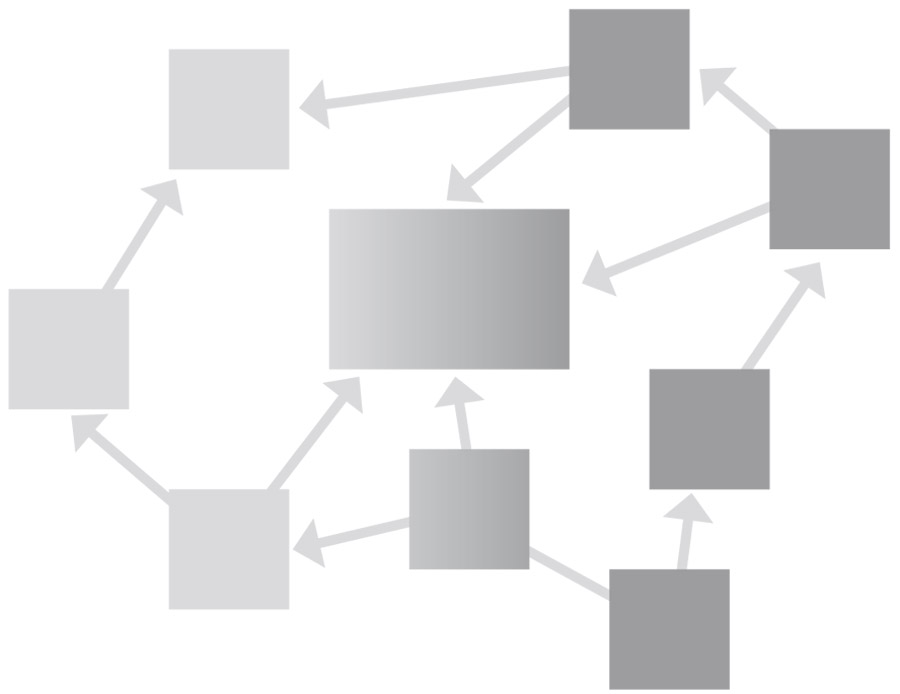
Introductory talk or introductory meeting
The introductory talk is held at the beginning of an audit (opening). The contents are: Introduction of the auditors; Explanation of the audit objectives; Overview of methods and procedures in auditing; Agreement on the time sequence; Clarification of the resources; Confidentiality; Reporting.
Involvement of people
The involvement of people is one of the eight quality management principles (see Quality management principles).
IPC
Integrated Process Control.
IPO
See Innovative process chain optimization
IQM
Integrated Quality Management.
IQNet
The International Certification Network, Bern (Switzerland). International network of 36 certification companies around the world, active since 1990.
Ishikawa
The Japanese Kaoru Ishikawa (1915-1989) is one of the pioneers and important individuals in quality science. His core activities were “company-wide quality control“, the “quality circle“ and particularly the cause and effect diagram that bears his name.
Ishikawa diagram
The Ishikawa or cause and effect diagram is a quality tool (Q7) for problem analysis in which the cause and the effect are separated from one another. The effect or problem is shown on the right-hand side of the chart, while the possible influencing factors or causes are listed on the left. The most common type of structure is a depiction of the 5M influencing factors: Milieu, method, man, material, machines. Further types of configuration are the 3-M influencing factors (milieu, measurability, management) and the 7M influencing factors (man, management, machine, method, material, measurability, milieu).

ISO
International Organization for Standardization, Geneva. International organization of standardization organizations. www.iso.org
ISO/TC 176
Technical Committee 176 on Quality Management and Quality Assurance. Responsible for the development of the ISO 9000 family of standards.
